I am a chemistry student and I'm doing a project about Erwin Schrodinger who came with the Wave-mechanical atomic model. Let's start!
Erwin Schrodinger: who was he?
| Erwin Schrodinger was born on 12 August 1887 and died 4 of January 1961. He was an Austrian physicist who came up with many important theories about the quantum theory. He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 and the Max Planck Medal in 1937. Erwin's father came from a Bavarian family which generations before had settled in Vienna. He was a highly gifted man with a broad education |
His history of discovering the wave mechanical model:
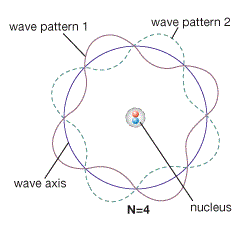
In 1926 Erwin Schrödinger combined the Bohr model with de Broglie's hypothesis. He proposed the electron was a 3-D waveform circling the nucleus in a whole number of wavelengths allowing the waveform to repeat itself as a stable standing wave representing the energy levels of the Bohr model.
A standing wave is one that does not transfer energy or move but it does undergo resonance. That is to say, it can absorb energy from a nearby source which is oscillating at a proper frequency. A standing wave must also have a wavelength such that a whole number of wave segments fit within its setting. If the number of wave segments isn’t a whole number then the wave will collapse.
Schrödinger suggested that de Broglie was correct about matter waves and the electrons are located in the atomic space according to standing wave frequencies. Therefore, the energy needed to change from one standing wave to another must be quantized in order to maintain a whole number of wavelengths and avoid collapsing.
In support of his hypothesis, Schrödinger developed a mathematical equation to describe the wave-like behavior of the electron. The Schrödinger wave equation not only gave the correct energy levels for the hydrogen atom, but also was somewhat useful in atoms with more than one electron.
What was his Atomic Theory?
The quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Where the cloud is most dense, the probability of finding the electron is greatest, and conversely, the electron is less likely to be in a less dense area of the cloud. Thus, this model introduced the concept of sub-energy levels.
How can this theory be proved?
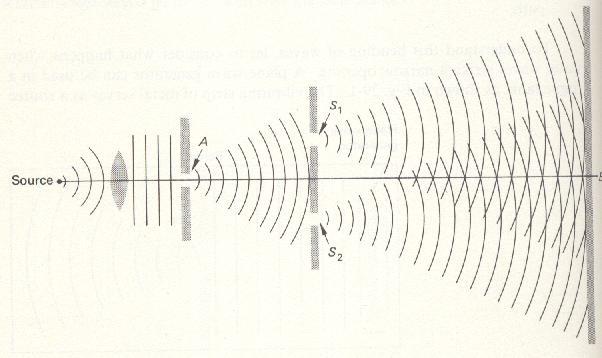
The double-slit experiment, is a demonstration that matter and energy can display characteristics of both waves and particles, and demonstrates the probabilistic nature of the electrons. The experiment belongs to a general class of "double path" experiments where a wave is split in two seperate waves which later on are combined again. Changes in path length of both waves results in phase shift causing an interference pattern.
Schrodinger’s equation:
the Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that describes how the quantum state of some physical system changes with time. It was formulated in late 1925, and published in 1926, by the Austrian physicist Erwin schrodinger.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed